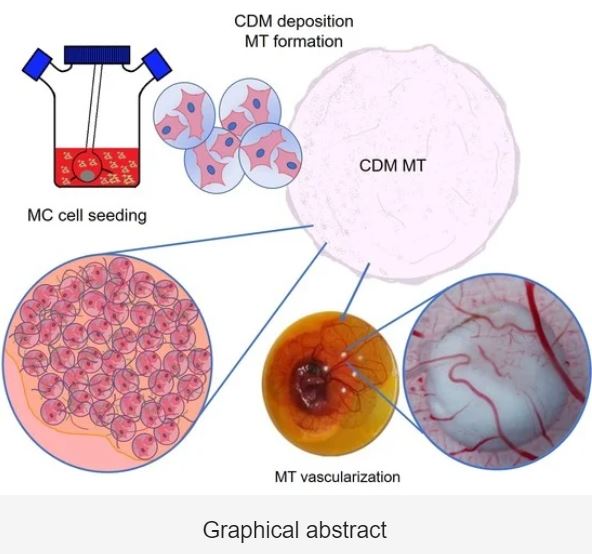
Abstract: Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine approaches use biomaterials in combination
with cells to regenerate lost functions of tissues and organs to prevent organ transplantation. However,
most of the current strategies fail in mimicking the tissue’s extracellular matrix properties. In
order to mimic native tissue conditions, we developed cell-derived matrix (CDM) microtissues
(MT). Our methodology uses poly-lactic acid (PLA) and Cultispher® S microcarriers’ (MCs’) as
scaffold templates, which are seeded with rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (rBM-MSCs).
The scaffold template allows cells to generate an extracellular matrix, which is then extracted for
downstream use. The newly formed CDM provides cells with a complex physical (MT architecture)
and biochemical (deposited ECM proteins) environment, also showing spontaneous angiogenic
potential. Our results suggest that MTs generated from the combination of these two MCs (mixed
MTs) are excellent candidates for tissue vascularization. Overall, this study provides a methodology
for in-house fabrication of microtissues with angiogenic potential for downstream use in various
tissue regenerative strategies.
Keywords: poly-lactic acid microcarriers; Cultispher® S; rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells;
microtissue; cell-derived matrix; angiogenesis
Link to the publication here.
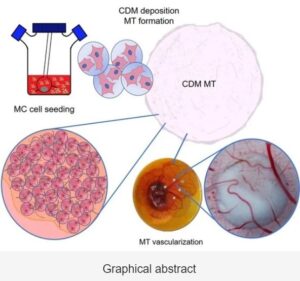 Abstract: Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine approaches use biomaterials in combination
Abstract: Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine approaches use biomaterials in combination
with cells to regenerate lost functions of tissues and organs to prevent organ transplantation. However,
most of the current strategies fail in mimicking the tissue’s extracellular matrix properties. In
order to mimic native tissue conditions, we developed cell-derived matrix (CDM) microtissues
(MT).